400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
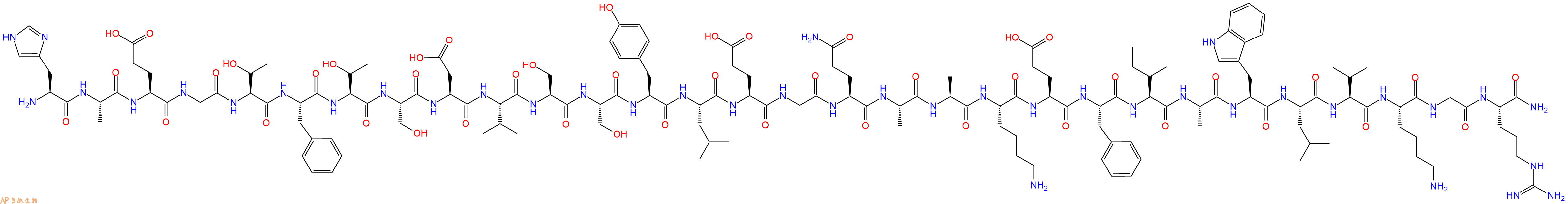
Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 (7-36) Amide是一种强效葡萄糖依赖性促胰岛素肽,它是通过肠道L细胞中胰高血糖素原的翻译后加工而产生的。
编号:196604
CAS号:107444-51-9/89750-14-1
单字母:H2N-HAEGTFTSDVSSYLEGQAAKEFIAWLVKGR-CONH2
GLP-1(7-36), amide 是刺激胰岛素分泌的生理性肠降血糖素。
Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 (7-36) Amide是一种强效葡萄糖依赖性促胰岛素肽,它是通过肠道L细胞中胰高血糖素原的翻译后加工而产生的。
GLP-1是一种强效胰岛素促分泌剂,对β细胞的葡萄糖依赖性胰岛素分泌途径具有多种协同作用。
GLP-1 is a potent insulin secretagogue that has multiple synergetic effects on the glucose-dependent insulin secretion pathways of the beta-cell.
This is an incretin hormone that causes glucose dependent release of insulin by pancreatic beta cells. It is the cleavage product of GLP-1 (1-36) amide peptide.\xa0\xa0This\xa0peptide, human GLP-1 (7–36), shares the same sequence with preproglucagon (78-107), amide, human.
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) is a peptide hormone that belongs to the glucagon family. It is a 36 amino acid polypeptide and is naturally synthesized in the ileum of humans, pigs, and cows. GLP-1 is an activator of ion channels, which are protein structures that regulate the flow of ions across cell membranes. This hormone also has been shown to inhibit the activity of protein interactions at the cell membrane or ligand binding to receptors.\n\nGlucagon-like Peptide 1 (Human, 7-36 Amide) (CAS No. 107444-51-9) is a research tool that can be used for pharmacological studies as well as for antibody production. It has been shown to activate ion channels in cells and inhibit protein interactions at the cell membrane or ligand binding to receptors.
| DOI | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 10.1210/endo.140.11.7143 | Glucagon-like peptide-1-(7-36)amide is transformed to glucagon-like peptide-1-(9-36)amide by dipeptidyl peptidase IV in the capillaries supplying the L cells of the porcine intestine | 下载 |
| 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91194-9 | Glucagon-like peptide-1 7-36: a physiological incretin in man | 下载 |
| 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17986.x | Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV hydrolyses gastric inhibitory polypeptide, glucagon-like peptide-1(7-36)amide, peptide histidine methionine and is responsible for their degradation in human serum | 下载 |
| 10.1007/BF00401145 | Normalization of fasting hyperglycaemia by exogenous glucagon-like peptide 1 (7-36 amide) in type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetic patients | 下载 |