400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研

β-Amyloid (1-42)由 42 个氨基酸组成的肽,其在阿尔茨海默病的发病机制中起关键作用。
编号:114789
CAS号:107761-42-2
单字母:H2N-DAEFRHDSGYEVHHQKLVFFAEDVGSNKGAIIGLMVGGVVIA-OH
β-Amyloid (1-42)由 42 个氨基酸组成的肽,其在阿尔茨海默病的发病机制中起关键作用。
淀粉样β-肽(1-42)(Aβ42)是一种42个氨基酸的肽,在阿尔茨海默病(AD)的发病机制中起着关键作用。
发病机制中的主要有害作用可能由Aβ42调节,Aβ42作为基因转录的阻遏物或激活物,导致进一步的突触功能损伤和神经元变性。
当Aβ42升高到2.5μM时,SH-SY5Y细胞的活力降低到65%。使用染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)和qRT-PCR分析,用具有LRP1和KAI1启动子的Aβ42相关肽处理SH-SY5Y细胞并增加APP mRNA水平,而无毒的Aβ42G33A肽作为大量存在于细胞核中的对照组,对mRNA表达没有任何影响。与几种不同长度的肽相比,Aβ42处理后其前体基因APP的转录和表达独家增加。
β42被认为是调节细胞功能的重要作用。
Amyloid β-Peptide (1-42) (Aβ42) human is a 42-amino acid peptide that plays a key role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease (AD).
The main deleterious effects in the pathogenesis are probably regulated by Aβ42, which acts as a repressor or activator of gene transcription causing further synaptic function damage and neuronal degeneration .
Aβ42 reduced the viability of SH-SY5Y cells to 65% when it rose to 2.5 μM. Using the chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and qRT-PCR assays, treatment of SH-SY5Y cells with Aβ42 associated peptide with both LRP1 and KAI1 promoters and increased APP mRNA levels, while the nontoxic Aβ42 G33A peptide, as a control group which presents in the nucleus abundantly, did not have any influence on mRNA expression. The exclusive increase of transcription and expression of its precursor gene APP was found with the treatment of Aβ42, compared with several different lengths of peptides .
Aβ42 is regarded as an important role in modulating the function of voltage-gated Ca2+- and K+-channels of the surface neuronal membranes. Application of Aβ42 with desired concentrations (1 to 10 μM) in the perfusing medium had no impact on delayed rectifier K+-current and leakage current, while enhanced inactivation of Ca2+-current and blocked Ca2+-dependent K+-current .
β1-42,淀粉样前体蛋白的42个残基片段,已被发现是阿尔茨海默病和晚期唐氏综合征患者大脑中形成的老年斑的主要成分。Aβ1-42在生理pH值下容易形成神经毒性低聚物。另一方面,该肽具有抗菌活性。该肽的序列对应于人、牛、犬、猫、绵羊、豚鼠和兔Aβ42的序列。该肽已被用于通过荧光相关光谱检测阿尔茨海默病患者脑脊液中的淀粉样β蛋白多聚体。关于Aβ1-42单体和原纤维制备的详细描述,请参阅Jan、Hartley和Lashuel、Stine等人(2011)以及Broersen及其同事的论文。Ryan等人的研究结果表明,10%的氨比HFIP更有效地分解Aβ42。
Aβ 1-42, 42-residue fragment of amyloid precursor protein, has been found to be a major constituent of the senile plaques formed in the brains of patients with Alzheimer’s disease and late Down’s syndrome. Aβ 1-42 readily forms neurotoxic oligomers at physiological pH. On the other hand, the peptide shows antimicrobial activity. The sequence of this peptide corresponds to the sequence of human, bovine, canine, feline, ovine, guinea pig, and rabbit Aβ42. The peptide has been used to detect amyloid β-protein multimers in the cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s disease patients through fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. For detailed descriptions of the preparation of Aβ 1-42 monomers and protofibrils please see the papers of Jan, Hartley, and Lashuel, Stine et al. (2011), and of Broersen and colleagues. The findings of Ryan et al. indicate that 10% ammonia disaggregates Aβ42 more efficiently than HFIP.
β-Amyloid (1-42) (Amyloid β-peptide (1-42)), human,一种未经 HFIP 处理过的由 42 个氨基酸组成的肽,是一种具有脑渗透性的淀粉样蛋白片段,可用于阿尔茨海默病和唐氏综合征的研究。β-Amyloid (1-42), human 以单体形式存在时具有抗氧化和神经保护作用。β-Amyloid (1-42), human 在经过 HFIP 单体化处理和用 DMSO 溶成母液后,一方面在 4 ℃ 孵育形成可溶性寡聚体 (AβOs),具有突触毒性和神经毒性;另一方面,可在 37℃ 孵育形成不溶性纤维,神经毒性较低,参与氧化损伤过程。Aβ42 寡聚体可与多种神经元表面受体 (如 PrPc、mGluR5、NMDA 受体等) 结合,通过激活下游信号通路引发氧化应激、钙稳态失衡和突触毒性,导致神经元功能障碍和死亡。
Amyloid-β peptide (Aβ)被认为是阿尔茨海默病发病机制中的关键因素。研究表明,Aβ能够调控神经元表面膜上电压门控Са2+通道和K+通道的功能[2- 6,8-13,15]。这种调节作用主要通过三种机制实现:1)Aβ与通道蛋白的直接相互作用;2)通过调节通道蛋白磷酸化水平产生的间接效应;3)激活基因组并增加膜通道蛋白密度。尽管该领域已有大量研究,但仍有诸多未解之谜。特别是关于Aβ对Ca2+通道失活及Ca2+激活的K+通道电导的影响机制仍不明确。
FA 的失调与阿尔茨海默病(AD)的发展密切相关。研究发现,阿尔茨海默病患者及动物模型中FA水平升高会引发认知功能障碍,但其具体作用机制仍不明确。最新研究揭示:淀粉样蛋白β(Aβ)丝氨酸8/26位点的氧化去甲基化会诱导FA生成,且FA与Aβ单体β转角处的赖氨酸28残基交联形成Aβ二聚体,从而加速体外实验中的Aβ寡聚化和纤维化过程。值得注意的是,当Aβ42突变体在丝氨酸8/26和赖氨酸28位点发生突变时,其自身聚集能力被完全抑制。此外,Aβ通过抑制甲醛脱氢酶(FDH)活性导致FA积累,而过量的FA则会通过促进Aβ寡聚体和纤维形成,在体外和体内实验中双重刺激Aβ聚集。研究发现,使用甲醛清除剂硫酸氢钠(NaHSO3)或辅酶Q10降解FA,可有效抑制Aβ聚集、减轻神经毒性,并改善APP/PS1小鼠的认知功能。本研究证实内源性FA对Aβ自聚集具有关键作用,清除FA或可成为治疗AD的有效策略。
FA 的降解可减少Aβ蛋白聚集并改善APP/PS1小鼠的记忆缺陷。a通过气相色谱-串联质谱联用技术(GC-MS/MS)检测辅酶Q10与FA的化学反应。b通过活体动物成像系统使用NaFA荧光成像检测脑内FA水平。
参考文献
[1]. Solntseva EI, et al. Impact of amyloid-β peptide (1-42) on voltage-gated ion currents in molluscan neurons. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2011 Oct;151(6):671-4.
[2]. Barucker C, et al. Nuclear translocation uncovers the amyloid peptide Aβ42 as a regulator of gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 2014 Jul 18;289(29):20182-91.
[3]. Stefania Sabella, et al. Capillary electrophoresis studies on the aggregation process of beta-amyloid 1-42 and 1-40 peptides. Electrophoresis. 2004 Oct;25(18-19):3186-94.
[4]. Porzoor A, et al. Pretreatment of chemically-synthesized Aβ42 affects its biological activity in yeast. Prion. 2014;8(6):404-10.
[5]. Zou K, et al. A novel function of monomeric amyloid beta-protein serving as an antioxidant molecule against metal-induced oxidative damage. J Neurosci. 2002 Jun 15;22(12):4833-41.
[6]. Peters C, et al. Alzheimer's Aβ interacts with cellular prion protein inducing neuronal membrane damage and synaptotoxicity. Neurobiol Aging. 2015 Mar;36(3):1369-77.
[7]. Yao ZX, et al. Function of beta-amyloid in cholesterol transport: a lead to neurotoxicity. FASEB J. 2002 Oct;16(12):1677-9.
[8]. Jancsó G, et al. Beta-amyloid (1-42) peptide impairs blood-brain barrier function after intracarotid infusion in rats. Neurosci Lett. 1998 Sep 4;253(2):139-41.
[9]. Bourgade K, et al. β-Amyloid peptides display protective activity against the human Alzheimer's disease-associated herpes simplex virus-1. Biogerontology. 2015 Feb;16(1):85-98.
[10]. Fu L, et al. Comparison of neurotoxicity of different aggregated forms of Aβ40, Aβ42 and Aβ43 in cell cultures. J Pept Sci. 2017 Mar;23(3):245-251.
[11]. Wang H, et al. Amyloid-beta1-42 induces reactive oxygen species-mediated autophagic cell death in U87 and SH-SY5Y cells. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;21(2):597-610.
[12]. Fei X, et al. Degradation of FA reduces Aβ neurotoxicity and Alzheimer-related phenotypes. Mol Psychiatry. 2021 Oct;26(10):5578-5591.
"Beta Amyloid peptides, also called Amyloid beta peptides (Abeta peptides) are the main component of amyloid peptide plaques in the brain of patients with Alzheimers disease. sb-PEPTIDE provides a broad range of chemically synthesized\xa0amyloid beta peptides\xa0for Alzheimers disease research. We supply Abeta peptides of different lengths and point-mutated versions. Do not hesitate to contact us for any information."
"Key subunit of extracellular plaques found in the brains of patients with Alzheimers disease; Hydrochloride salt"
"Amyloid β-Protein (1-42) is a fragment of the amyloid beta protein that is thought to be a major contributor to the development of Alzheimers disease. Amyloid β-Protein (1-42) has been shown to have neuroprotective effects, as it reduces cell death in the brain and preserves memory. It binds to the β-catenin protein in neurons and protects against oxidative stress by reducing production of reactive oxygen species. This molecule also reduces microglia activation and tnf-α levels, which may reduce inflammation. Amyloid β-Protein (1-42) is found in plants such as pueraria lobata, and has been used for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine for its anti-inflammatory properties."
"Key subunit of extracellular plaques found in the brains of patients with Alzheimers disease. TFA salt; 95%."
Amyloid beta-protein (Aβ) is a peptide that is found in the human brain. It is one of the major components of amyloid plaque, which are deposits of a protein fragment in the brain that form as a result of aging and Alzheimer’s disease. It is produced by cleavage of the amyloid precursor protein (APP). Aβ has been shown to be toxic to cells, causing them to die. This toxicity may be due to its ability to inhibit ATP production and increase oxidative stress. Aβ can also induce apoptosis by binding to receptors on cell surfaces and activating intracellular signaling pathways. These events lead to activation of caspases, which are proteolytic enzymes that contribute to programmed cell death.
"Amyloid β-peptide (Aβ) has been identified as the key subunit of the extracellular plaques found in the brains of patients with Alzheimers disease (AD) and Downs syndrome (DS). Aβ has therefore been extensively studied as a potential target for treatment of AD.Aβ is formed from the cleavage of the large, transmembrane protein- APP (amyloid precursor protein). Cleavage of APP by β- and then γ-secretases results in the formation of Aβ. Aβ can aggregate to produce amyloid-β oligomers, which are thought to be highly neurotoxic. Over time Aβ can further aggregate to produce the characteristic senile plaques present in AD and DS.Aβ can be degraded by enzymes such as neprilysin, insulin degrading enzyme or endothelin converting enzyme. At physiological levels Aβ may be involved in controlling synaptic activity and neuronal survival."
淀粉肽背景:β淀粉样蛋白(Aβ或Abeta)是从淀粉样前体蛋白加工而成的含有36–43个氨基酸的多肽。Aβ是与阿尔兹海默病相关的淀粉样蛋白斑的成分。已有证据表明,Aβ是一个多功能肽,具有显著的非病理性活性。Aβ是阿尔兹海默病患者脑中发现的沉积物的主要成分。在散发性阿尔兹海默病患者的脑中,Aβ的水平升高,造成脑血管病变和神经毒性。Aβ蛋白是由β和γ分泌酶的连续作用而产生的。γ分泌酶产生Aβ肽的C末端,在APP的转膜结构域切割,可以产生许多36-43个氨基酸残基长度的异构体,最常见的异构体是Aβ40和Aβ42。更长形式的Aβ在内质网中切割产生,而更短形式的Aβ在反面高尔基网中产生。
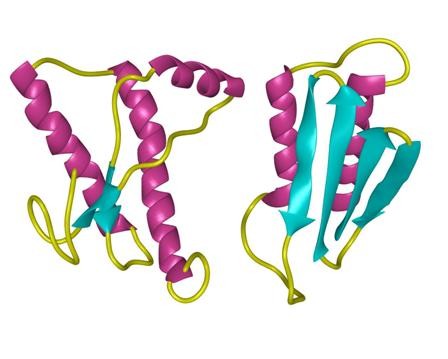
structure of Amyloid β-Peptide (1-40) (human)
淀粉样蛋白肽的 定义淀粉样蛋白 是丝状蛋白质沉积物,大小从纳米到微米不等,并且由肽β链的平行或反平行排列形成的聚集的肽β折叠构成。
结构特征:使用固态NMR(SSNMR),与计算能量最小化过程结合,Tycko和合作者已经提出从淀粉状蛋白肽SS(Aß1-40)的40个残基的形式形成的淀粉样蛋白原纤维的结构在pH 7.4和24 o C在静止条件下。在这种结构中,每个Aß1-40分子在原纤维的核心区域贡献一对ß链,大约跨越残基12-24和30-40。这些由回路25-29连接的链不是同一张ß-sheet的一部分,但参与同一原丝内两个不同的ß-sheets的形成。不同的Aß分子2、3至少从第9到39位残基以平行排列和对齐的方式相互堆叠。通过调用其他实验约束,例如使用透射电子显微镜(TEM)观察到的原丝直径和单位质量通过扫描透射电子显微镜(STEM)1、2测得的长度表明,单个原丝是由四个ß片组成的,它们之间的距离约为10Å。
作用模式:阿尔茨海默氏病(AD)是淀粉样蛋白丝状沉积物的结果,淀粉状蛋白沉积物在分子水平上定义该疾病,发生在神经周膜,轴突,树突和神经元末端,如神经原纤维缠结(NFT),在细胞外神经纤维中淀粉样斑块(APC),以及周围的血管称为淀粉样嗜血性血管病(ACA)。淀粉样蛋白沉积物显然发生在发展NFT的神经元末端区域。已经表明,APC和ACA的主要成分已被证明是4.5kDa的淀粉样蛋白,最初被称为“β-蛋白”或“淀粉样蛋白A4”,我们现在将其称为“βA4”。
功能:钙失调和膜破坏是可溶性淀粉样蛋白低聚物普遍存在的神经毒性机制:进行了一项研究,以研究Ca 2+信号转导可能参与淀粉样蛋白诱导的细胞毒性,疾病相关淀粉样蛋白(β,病毒,胰岛淀粉样蛋白)的均质制剂制备了处于各种聚集状态的多肽,聚谷氨酰胺和溶菌酶),并测试了它们对加载fluo-3的SH-SY5Y细胞的作用。寡聚形式的所有淀粉样蛋白的应用(0.6-6 µg / ml)迅速(约5 s)使细胞内Ca 2+升高,而等量的单体和原纤维则没有。细胞内Ca 2+耗尽后,Abeta42低聚物引起的Ca 2+信号持续存在店,和小信号仍留在钙2 + -游离介质,指示从细胞外和细胞内Ca贡献2+源。膜对Ca 2+的渗透性增加不能归因于内源性Ca 2+通道的活化,因为反应不受强力的Ca 2 +-通道阻滞剂钴的影响。取而代之的是,观察到Abeta42和其他低聚物引起阴离子荧光染料的快速细胞泄漏,这表明膜通透性普遍提高。导致的离子和分子通量失调可能为许多淀粉样变性疾病中Ca 2+失调提供了由低聚物介导的毒性的常见机制。离子起着至关重要的作用,因为它们的跨膜浓度梯度很强,并且参与了细胞功能障碍和死亡。
2型糖尿病中的胰岛淀粉样蛋白和毒性低聚物假说: 2型糖尿病(T2DM)的特征是胰岛素抵抗,胰岛素分泌缺陷,β细胞量减少,β细胞凋亡增加和胰岛淀粉样蛋白。胰岛淀粉样蛋白源自胰岛淀粉样蛋白多肽(IAPP,胰岛淀粉样多肽),该蛋白是通过胰β细胞与胰岛素共表达和共分泌的蛋白。与其他淀粉样蛋白一样,IAPP具有形成膜渗透性毒性低聚物的倾向。越来越多的证据表明,这些有毒的寡聚体而不是这些蛋白质的细胞外淀粉样蛋白形式,是导致神经退行性疾病中神经元丢失的原因。有人提出,胞内IAPP寡聚物的形成可能会导致T2DM 6中的β细胞丢失。
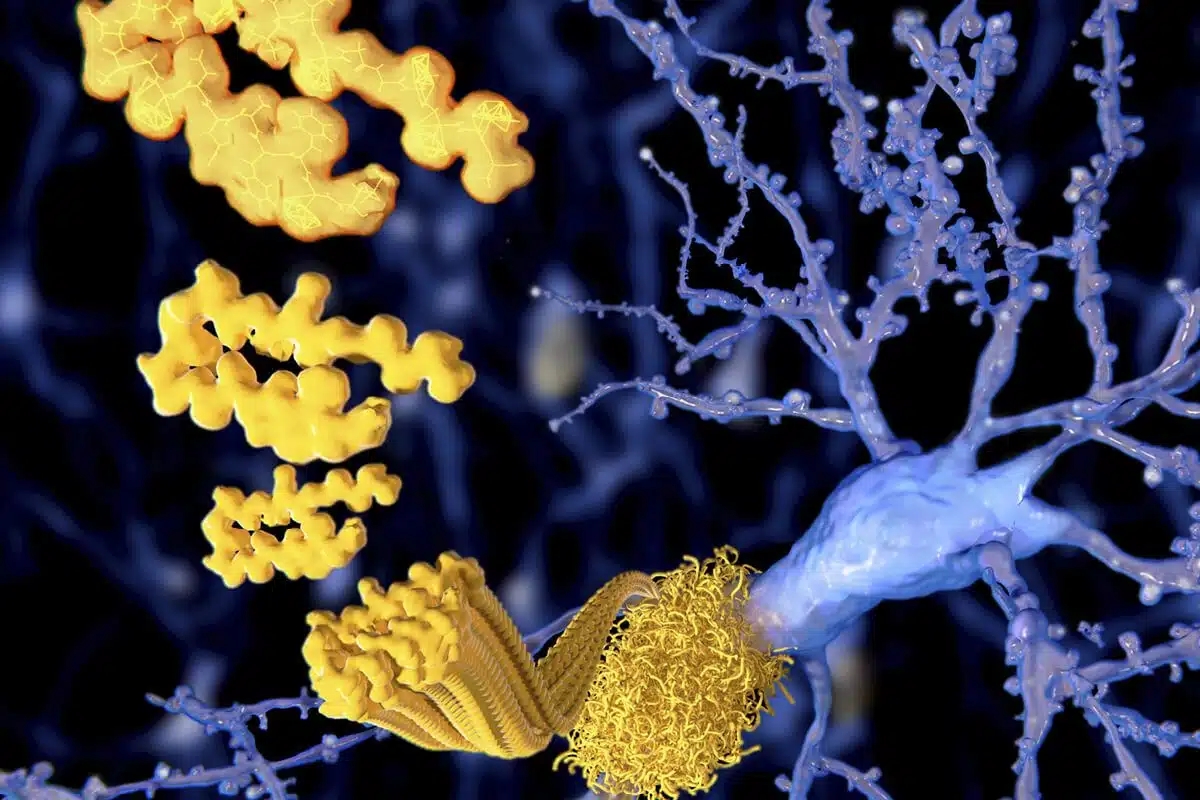
Extracellular amyloid-β peptide deposition into cerebellar plaques and formation of intracellular neurofibrillary fibers accompanied by the loss of neurons are characteristic histopathological lesions found in the brains of Alzheimer‘s disease patients. Individuals suffering from this disease show a gradual loss of cognitive functions and disturbances in behavior. Apart from some rare familial forms of the disease, the onset of Alzheimer‘s disease is usually above 60 years. Since the risk to develop the disease increases with age, Alzheimer‘s disease has turned into a major health and social problem in “first world” countries with an increasing proportion of older people, and is going to become one in emerging states. In this brochure we present amyloid peptides and related products for Alzheimer‘s disease research.
ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE
Alzheimer‘s disease (AD) is the prevalent cause of dementia in elderly people and has become one of the leading causes of death in developed countries together with cardiovascular disorders, cancer, and stroke. It is estimated that more than 46 millions of people suffer from AD all over the world. As age advances, the risk for developing AD increases. The frequency of AD at the age of 60-64 is about 1% and doubles approximately every five years. By the age of 90 and older, approximately 50% of the population suffers from this disease. AD is an irreversible and progressive neurodegenerative disorder. Symptoms include gradual loss of cognitive functions such as memory, verbal and visuospatial abilities, changes in personality, behavior, and activities of daily living. AD patients in the final stages are completely dependent on the care of others.
The characteristic lesions in the brains of AD patients were first described by the German neuropsychiatrist Alois Alzheimer in 1906 during the post-mortem examination of a mentally ill patient whose deterioration he had observed until her death. The lesions consisted of dense extracellular deposits, now designated as neuritic or senile plaques, and intracellular dense bundles of fibrils, which are now known as neurofibrillary tangles.
Currently, diagnosis of AD with adequate testing is approximately 90% accurate. It is based on the exclusion of a variety of diseases causing similar symptoms and a careful neurological and psychiatric examination, as well as neuropsychological testing. Imaging technologies for detecting amyloid plaques and tangles in vivo are becoming more precise and thus a valuable additional tool. Numerous potential biomarkers as α1 -antitrypsin, complement factor H, α2 -macroglobulin, apolipoprotein J, and apolipoprotein A-I for diagnosing AD are being evaluated. However, post-mortem histopathological examination of the brain is still the only definite diagnosis of this disease.
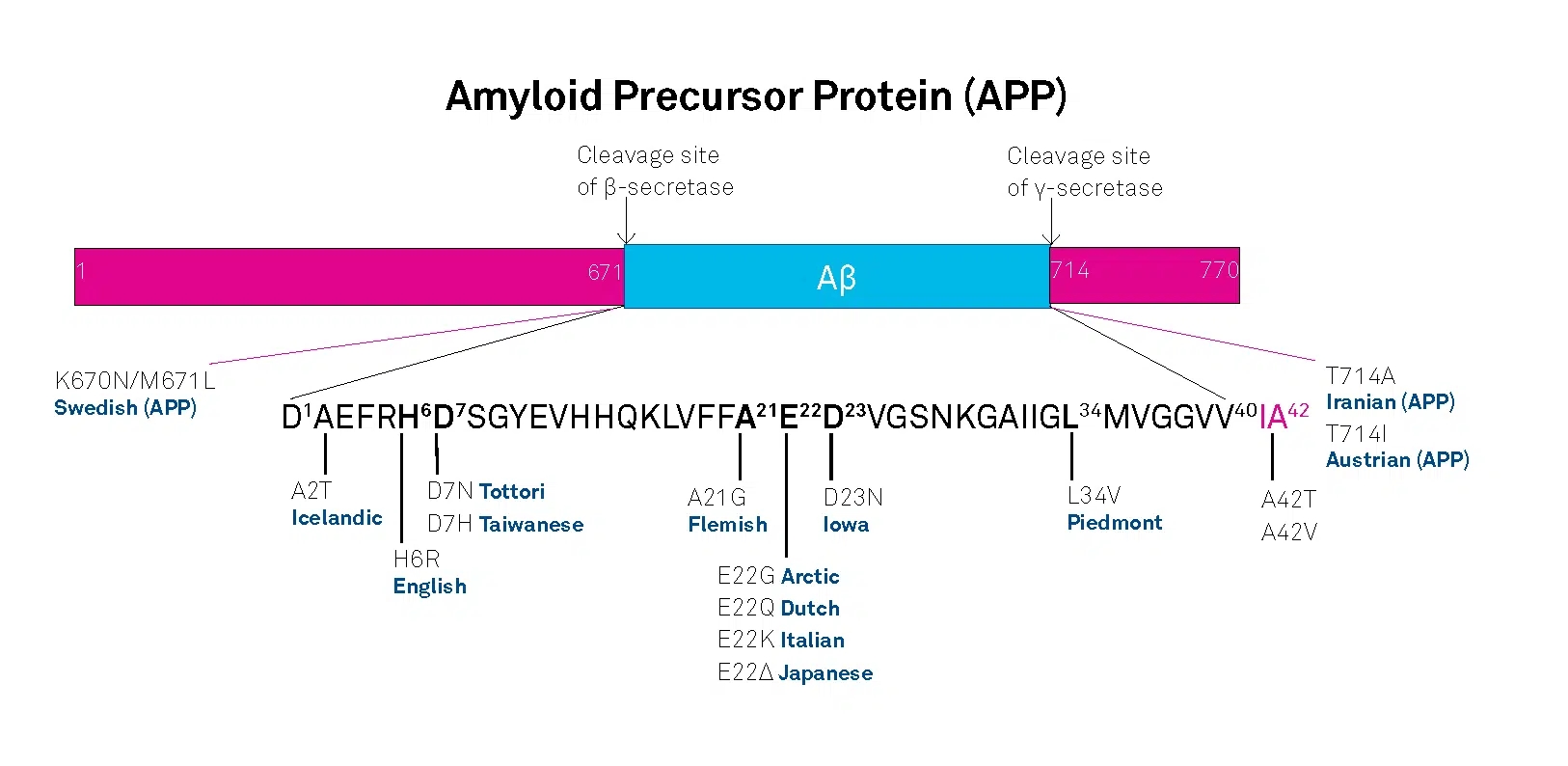
AD can be either inherited or sporadic. The inherited or familial AD is rare and comprises only 5-10% of all cases. Autosomal dominant mutations in the amyloid β/A4 protein precursor (APP) gene on chromosome 21 and the presenilin-1 or -2 genes on chromosomes 14 and 1, respectively, have been attributed to the early onset (before the age of 65) of this disease.
APP belongs to the type-1 integral membrane glycoproteins with at least 10 isoforms generated by alternative splicing of the 19 exons. The predominant transcripts are APP695, APP751, and APP770. A number of mutations within the APP gene have been detected in families with an inherited risk for early onset of AD. Usually, they are named after the region, in which they have been detected, e.g. the London APP717 mutations (V717I, V717F, V717G), the Swedish APP670/671 double mutation (K670N/M671L), the Flemish APP692 mutation (A692G), or the Dutch APP693 mutation (E693Q). The Swedish mutation of the β-secretase cleavage site of APP and mutations of positions 692-694 (Aβ 21-23), which strongly influence the aggregation behavior of Aβ, have been studied intensively.
A choice of relevant mutations in the Aβ region of APP is assembled in the table below.
| Exchanged Position in APP | Exchanged Position in Aβ | Designation |
|---|---|---|
| A673T | A2T | Icelandic |
| H677R | H6R | English |
| D678H | D7H | Taiwanese |
| D678N | D7N | Tottori |
| A692G | A21G | Flemish |
| E693D | E22∆ | Osaka |
| E693G | E22G | Arctic |
| E693Q | E22Q | Dutch |
| E693K | E22K | Italian |
| D694N | D23N | Iowa |
| L705V | L34V | Piedmont |
The presenilins are another group of proteins involved in the development of AD. Presenilins are integral membrane proteins with eight transmembrane domains localized in the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. A multitude of mutations within the presenilin-1 and two within the presenilin-2 gene account for most of the cases of early onset of AD.
Genetic factors may contribute as well to the late onset of AD. Increased susceptibility is associated with the expression of different apolipoprotein E (ApoE) isoforms due to the polymorphism in the APOE gene on chromosome 19. In the central nervous system, ApoE has been implicated in growth and repair during development or after injury. Carriers of the APOEε4 allele show a higher risk in developing the disease than carriers of the other two possible alleles APOEε2 and APOEε3. The ApoEε4 effect seems to be dose-dependent since individuals with two of these alleles seem to be at two-fold higher risk to develop the disease than those with one allele. Polymorphisms of the α2 -macroglobulin gene on chromosome 12 and the gene coding low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1), LRP1-C/T, have also been suggested to be a risk factor for the late onset of AD. However, further studies in this field are required.
A number of additional, most diverse risk factors have been proposed. These include gender, ethnic group, head trauma, cardiovascular diseases, and educational level.
AD THERAPEUTIC STRATEGIES RELY ON DETAILED KNOWLEDGE OF THE MOLECULES INVOLVED
Women, Hispanics, individuals who have experienced a head trauma earlier in life, and persons who suffer from cardiovascular diseases appear to have a higher risk of developing the disease.
The etiology of AD is still not completely understood. Initial research focused upon determining the molecular structure of the senile plaques and the neurofibrillary tangles originally described by Alois Alzheimer. The main constituents of the senile plaques were identified as cleavage products of APP, designated as amyloid β-peptides (Aβ peptides).
Depending on the composition and the fraction of fibrillar to non-fibrillar forms of these amyloid peptides, several kinds of senile plaques can be distinguished. Three types of proteases, α-secretase, β-secretase (or β-site APP-cleaving enzyme, BACE), and γ-secretase are involved in APP processing. APP can either be processed by the α- and γ- or by the β- and γ-secretases. The major two amyloid peptides identified in senile plaques, amyloid β-protein (1-40) (Aβ40) and amyloid β-protein (1-42) (Aβ42), are generated by successive proteolysis of APP by β- and γ-secretases. Cleavage of APP by β-secretase results in the release of the extracellular N-terminal protein fragment known as soluble APP-β molecule (sAPP-β). Then, the membrane-retained APP is further processed within the transmembrane domain by γ-secretase to yield either Aβ40 or Aβ42. The formation of Aβ40 and Aβ42 is a normal process, and both peptides can be detected in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of healthy subjects.
In most studies, similar concentrations of Aβ40 have been measured in the CSF of both healthy controls and AD patients. On the other hand, Aβ42 concentrations in the CSF of AD patients are significantly lower than in normal controls, probably reflecting an increased deposition as insoluble plaques.
The neurofibrillary tangles found inside neurons of Alzheimer’s brains are composed of paired helical filaments whose main components are hyperphosphorylated forms of tau, a microtubule associated protein involved in promoting microtubule assembly and stabilization. Self-assembly into paired helical filaments is believed to be a result of hyperphosphorylation due to either the increased activity of protein kinases or the decreased activity of phosphatases.
Several lines of evidence support the view that the accumulation of Aβ42 in the brain is a primary event in the development of AD. Increased cerebral Aβ production appears to be characteristic for all the mutations within the APP and the presenilin genes of familial AD. In patients with Down syndrome (trisomy 21), elevated levels of APP and Aβ due to a third copy of the APP gene result in deposition of Aβ at an early age between 20 and 30.
Formation of neurofibrillary tangles is considered as a consequence of Aβ deposition with a further impact on the progression of the disease possibly due to disruption of axonal transport mechanisms in neurons.
The detailed knowledge about the molecules involved in AD has led to the development of several therapeutic strategies.
One strategy aims at the reduction of Aβ40 and Aβ42 by inhibition of either β- or γ-secretase activity or by clearance of Aβ in the brain by means of immunization with these peptides. Transition metals as Cu, Fe and Zn play an important role in the pathology of AD. Aggregation and neurotoxicity of Aβ are dependent on the presence of copper, so Cu-chelating agents showed promising effects in animal models. Another approach is the prevention of the cellular inflammatory response in the cerebral cortex elicited by the progressive accumulation of Aβ. Further preventive therapeutic strategies are based on the findings that cholesterol-lowering drugs such as statins and estrogen replacement therapy reduce the risk of developing AD. An additional treatment alternative would be the inhibition of the serine-threonine protein kinases, glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) and cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5), which are probably responsible for the phosphorylation of the tau protein. Inhibition of calpain, an enzyme showing increased activity in AD brains, led to promising results in animal studies. Calpain cleaves the CDK5 activator p35 leading to p25 formation and CDK5 overactivation.
Several acetylcholinesterase inhibitors such as tacrine, donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine have been approved for the treatment of mild to moderate AD by the FDA and other authorities. They act by reducing the deficits of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine associated with cognitive impairment in AD patients. The amantadine derivative memantine, an NMDA receptor antagonist, which was already used for the treatment of moderate to severe AD in Europe, has gained approval in the United States by the FDA as well.
A promising drug candidate, the β-secretase inhibitor verubecestat (MK-8931) developed for the management of mild to moderate AD, has moved to phase III. Moreover, the BACE inhibitor AZD3293 showed encouraging results in clinical studies. Antibodies as aducanumab and solanezumab, which have been designed to degrade plaques and lower the level of Aβ in the brain, have reached advanced stages of clinical testing for mild cases of AD.
Despite the many promising therapeutic approaches, AD still remains a major burden for the patients, their relatives, and the society.
| DOI | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 10.1002/elps.200406062 | Capillary electrophoresis studies on the aggregation process of beta-amyloid 1-42 and 1-40 peptides | 下载 |
| 10.1002/cbic.200700111 | Redox chemistry of copper-amyloid-beta: the generation of hydroxyl radical in the presence of ascorbate is linked to redox-potentials and aggregation state | 下载 |
| 10.1007/s10517-011-1412-y | Impact of amyloid-β peptide (1-42) on voltage-gated ion currents in molluscan neurons | 下载 |
| 10.1074/jbc.M114.564690 | Nuclear translocation uncovers the amyloid peptide Aβ42 as a regulator of gene transcription | 下载 |
| 10.1093/protein/gzr020 | A standardized and biocompatible preparation of aggregate-free amyloid beta peptide for biophysical and biological studies of Alzheimer's disease | 下载 |
| 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04426.x | A beta oligomers - a decade of discovery | 下载 |
| 10.1016/S0076-6879(06)13002-5 | Preparation of amyloid beta-protein for structural and functional studies | 下载 |
| 10.1007/978-1-60761-744-0_2 | Preparing synthetic Aβ in different aggregation states | 下载 |
| 10.7717/peerj.73 | Ammonium hydroxide treatment of Aβ produces an aggregate free solution suitable for biophysical and cell culture characterization | 下载 |
| 10.1038/nm0798-832 | Detection of single amyloid beta-protein aggregates in the cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer's patients by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy | 下载 |
| 10.1126/science.1925564 | A mutation in the amyloid precursor protein associated with hereditary Alzheimer's disease | 下载 |
| 10.1073/pnas.222681699 | Amyloid beta -protein (Abeta) assembly: Abeta 40 and Abeta 42 oligomerize through distinct pathways | 下载 |
| 10.1172/JCI25100 | The role of cerebral amyloid beta accumulation in common forms of Alzheimer disease | 下载 |
| 10.1074/jbc.M210207200 | In vitro characterization of conditions for amyloid-beta peptide oligomerization and fibrillogenesis | 下载 |