400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
含有天冬酰胺-甘氨酸-精氨酸 (NGR) 基序的肽,NGR peptide (NGR 肽) 可靶向肿瘤新生血管上皮细胞特异过量表达的 CD13 受体。
编号:200803
CAS号:651328-78-8;760947-20-4
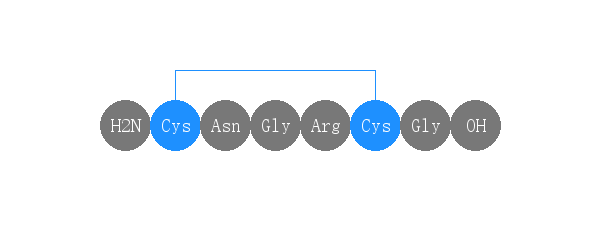
单字母:H2N-CNGRCG-OH(Disulfide Bridge:C1-C5)
| 编号: | 200803 |
| 中文名称: | CD13 受体靶向肽、NGR肽: NGR peptide、Aminopeptidase N Ligand (CD13) NGR peptide |
| 英文名: | NGR peptide、Aminopeptidase N Ligand (CD13) NGR peptide |
| 英文同义词: | Aminopeptidase N Ligand (CD13), NGR peptide |
| CAS号: | 651328-78-8;760947-20-4 |
| 单字母: | H2N-CNGRCG-OH(Disulfide Bridge:C1-C5) |
| 三字母: | H2N-Cys-Asn-Gly-Arg-Cys-Gly-OH(Disulfide Bridge:Cys1-Cys5) |
| 氨基酸个数: | 6 |
| 分子式: | C20H34N10O8S2 |
| 平均分子量: | 606.68 |
| 精确分子量: | 606.2 |
| 等电点(PI): | - |
| pH=7.0时的净电荷数: | 3.91 |
| 平均亲水性: | 0.3 |
| 疏水性值: | -0.63 |
| 消光系数: | - |
| 来源: | 人工化学合成,仅限科学研究使用,不得用于人体。 |
| 储存条件: | 负80℃至负20℃ |
| 标签: | 二硫键环肽 |
NGR peptide Trifluoroacetate 是含有天冬酰胺-甘氨酸-精氨酸 (NGR) 基序的肽,NGR peptide (NGR 肽) 可靶向肿瘤新生血管上皮细胞特异过量表达的 CD13 受体。
NGR peptide Trifluoroacetate containing the asparagine-glycine-arginine (NGR) motif is recognized by CD13/aminopeptidase N (APN) receptor isoforms that are selectively overexpressed in tumor neovasculature.
它是一种具有NGR(Asn-Gly-Arg)基序的肽,具有连接cys1和cys5的二硫键,并且已知除了存在KLA序列之外还具有抗菌特性。该肽与肿瘤细胞上的CD13结合,并显示出强大的细胞毒性和抗肿瘤细胞的活性。该肽显示出对肿瘤细胞的剂量依赖性抗增殖作用,并诱导细胞周期停滞在G2/M期和肿瘤细胞凋亡。含有NGR基序的肽可用于将细胞毒性药物、促凋亡肽和肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)递送到肿瘤血管系统中。
It is a peptide with NGR (Asn-Gly-Arg) motif, which has a disulfide bridge linking cys1 and cys5, and is known to have antimicrobial properties in addition to the presence of KLA sequences. The peptide binds to CD13 on tumor cells and shows strong cytotoxicity and activity against tumor cells. This peptide shows dose-dependent antiproliferation against tumor cells and induces cell cylce arrest at G2/M phases and apoptosis of the tumor cells. Peptides containing the NGR motif are useful in the delivery of cytotoxic drugs, pro-apoptotic peptides, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) into tumor vasculature.
含有天冬酰胺-甘氨酸-精氨酸(NGR)基序的三氟乙酸NGR肽可被在肿瘤新生血管中选择性过表达的CD13/氨基肽酶N(APN)受体亚型识别。CD13/氨基肽酶N(APN)受体[1]
NGR peptide Trifluoroacetate containing the asparagine-glycine-arginine (NGR) motif is recognized by CD13/aminopeptidase N (APN) receptor isoforms that are selectively overexpressed in tumor neovasculature. CD13/aminopeptidase N (APN) receptor[1]
NGR肽可以选择性地结合被免疫捕获或表达在细胞表面的APN/CD13,因此肿瘤归巢NGR肽的受体被推测为APN/CD13。据报道,NGR肽具有最高的肿瘤选择性。与NGR肽偶联的抗癌药物阿霉素(DOX)显示出比游离药物本身更强的抗肿瘤效果,且毒性更低[2]。
NGR peptide can selectively bind to APN/CD13 either immune-captured or expressed on the surface of cells, the receptor of the tumor-homing NGR peptide was suspected to be APN/CD13. The NGR peptide is reported to have the greatest tumor selectivity. An anti-cancer drug Doxorubicin (DOX) coupled to an NGR peptide displays enhanced anti-tumor effects with even lower toxicity than the free drug itself[2].
NGR肽体内成像不仅有助于更深入地了解NGR的靶向过程,包括生物分布和药代动力学,还能揭示与肿瘤进展和恶性程度相关的血管生成活性[2]。
NGR peptide imaging in vivo not only provides more insight into NGR's targeting process, including bio-distribution and pharmacokinetics, but also reveals angiogenic activities related to tumor progression and malignancy[2].
参考文献:
Enyedi KN, et al. NGR-peptide-drug conjugates with dual targeting properties. NGR-peptide-drug conjugates with dual targeting properties. [2]. Wang RE, et al. Development of NGR peptide-based agents for tumor imaging. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011;1(1):36-46.
二硫键广泛存在与蛋白结构中,对稳定蛋白结构具有非常重要的意义,二硫键一般是通过序列中的2个Cys的巯基,经氧化形成。
形成二硫键的方法很多:空气氧化法,DMSO氧化法,过氧化氢氧化法等。
二硫键的合成过程, 可以通过Ellman检测以及HPLC检测方法对其反应进程进行监测。
如果多肽中只含有1对Cys,那二硫键的形成是简单的。多肽经固相或液相合成,然后在pH8-9的溶液中进行氧化。
当需要形成2对或2对以上的二硫键时,合成过程则相对复杂。尽管二硫键的形成通常是在合成方案的最后阶段完成,但有时引入预先形成的二硫化物是有利于连合或延长肽链的。通常采用的巯基保护基有trt, Acm, Mmt, tBu, Bzl, Mob, Tmob等多种基团。我们分别列出两种以2-Cl树脂和Rink树脂为载体合成的多肽上多对二硫键形成路线:
二硫键反应条件选择
二硫键即为蛋白质或多肽分子中两个不同位点Cys的巯基(-SH)被氧化形成的S-S共价键。 一条肽链上不同位置的氨基酸之间形成的二硫键,可以将肽链折叠成特定的空间结构。多肽分 子通常分子量较大,空间结构复杂,结构中形成二硫键时要求两个半胱氨酸在空间距离上接近。 此外,多肽结构中还原态的巯基化学性质活泼,容易发生其他的副反应,而且肽链上其他侧链 也可能会发生一系列修饰,因此,肽链进行修饰所选取的氧化剂和氧化条件是反应的关键因素, 反应机理也比较复杂,既可能是自由基反应,也可能是离子反应。
反应条件有多种选择,比如空气氧化,DMSO氧化等温和的氧化过程,也可以采用H2O2,I2, 汞盐等激烈的反应条件。
空气氧化法: 空气氧化法形成二硫键是多肽合成中最经典的方法,通常是将巯基处于还原态的多肽溶于水中,在近中性或弱碱性条件下(PH值6.5-10),反应24小时以上。为了降低分子之间二硫键形成的可能,该方法通常需要在低浓度条件下进行。
碘氧化法:将多肽溶于25%的甲醇水溶液或30%的醋酸水溶液中,逐滴滴加10-15mol/L的碘进行氧化,反应15-40min。当肽链中含有对碘比较敏感的Tyr、Trp、Met和His的残基时,氧化条件要控制的更精确,氧化完后,立即加入维生素C或硫代硫酸钠除去过量的碘。 当序列中有两对或多对二硫键需要成环时,通常有两种情况:
自然随机成环: 序列中的Cys之间随机成环,与一对二硫键成环条件相似;
定点成环: 定点成环即序列中的Cys按照设计要求形成二硫键,反应过程相对复杂。在 固相合成多肽之前,需要提前设计几对二硫键形成的顺序和方法路线,选择不同的侧链 巯基保护基,利用其性质差异,分步氧化形成两对或多对二硫键。 通常采用的巯基保护 基有trt, Acm, Mmt, tBu, Bzl, Mob, Tmob等多种基团。
| DOI | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 10.1371/journal.pone.0178632 | NGR-peptide-drug conjugates with dual targeting properties | 下载 |