400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
ETA/ ETB受体激动剂,血管收缩剂。
编号:147759
CAS号:
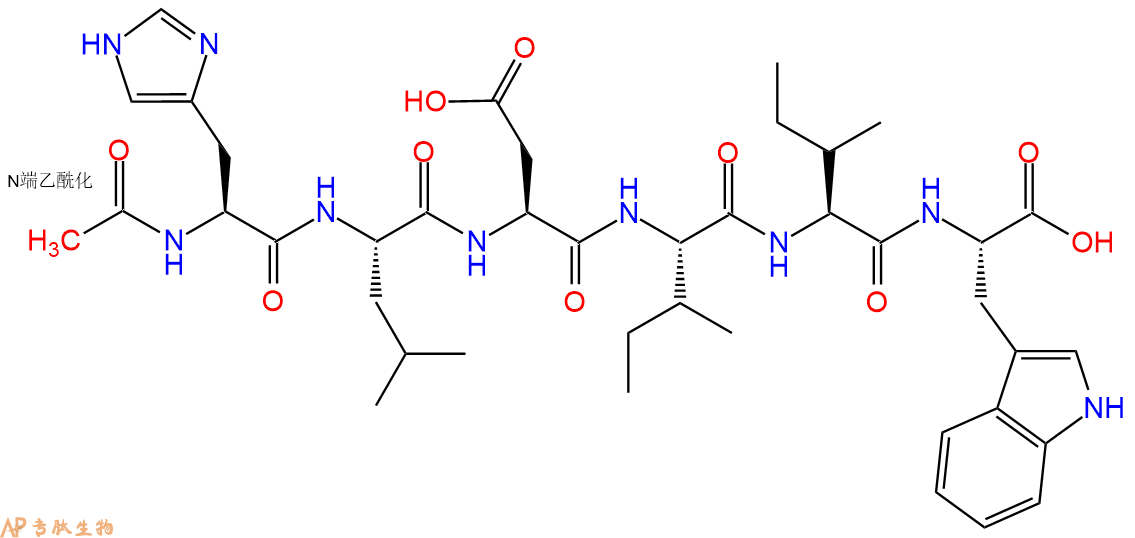
单字母:Ac-HLDIIW-OH
| 编号: | 147759 |
| 中文名称: | ETA/ ETB受体激动剂,血管收缩剂:Ac-Endothelin-1(16-21), human |
| 英文名: | Ac-Endothelin-1(16-21), human |
| 单字母: | Ac-HLDIIW-OH |
| 三字母: | Ac N端乙酰化封端,一种常见的修饰方式,常用于模拟蛋白质中的肽片段。 -HisL-组氨酸:histidine。系统命名为(2S)-氨基-3-(4-咪唑基)丙酸。其侧链带有弱碱性的咪唑基,为编码氨基酸。是幼小哺乳动物的必需氨基酸。符号:H,His。 -LeuL-亮氨酸:leucine。系统命名为(2S)-氨基-4-甲基戊酸。是编码氨基酸。是哺乳动物的必需氨基酸。符号:L,Leu。 -AspL-天冬氨酸:aspartic acid。系统命名为(2S)-氨基-丁二酸。是编码氨基酸,又是神经递质。符号:D,Asp。D-天冬氨酸存在于多种细菌的细胞壁和短杆菌肽A中。 -IleL-异亮氨酸:isoleucine。系统命名为(2S)-氨基-(3R)-甲基戊酸。是编码氨基酸。有两个手性碳原子,是哺乳动物的必需氨基酸。符号:I,Ile。 -IleL-异亮氨酸:isoleucine。系统命名为(2S)-氨基-(3R)-甲基戊酸。是编码氨基酸。有两个手性碳原子,是哺乳动物的必需氨基酸。符号:I,Ile。 -TrpL-色氨酸:tryptophan[e]。系统命名为(2S)-氨基-3-(3-吲哚基)丙酸。是编码氨基酸,哺乳动物的必需氨基酸。符号:W,Trp。某些抗菌素中含有 D-色氨酸。 -OHC端羧基:C-terminal carboxyl group。在肽或多肽链中含有游离羧基的氨基酸一端。在表示氨基酸序列时,通常将C端放在肽链的右边。 |
| 氨基酸个数: | 6 |
| 分子式: | C41H59O10N9 |
| 平均分子量: | 837.96 |
| 精确分子量: | 837.44 |
| 等电点(PI): | 5.21 |
| pH=7.0时的净电荷数: | -0.76 |
| 平均亲水性: | -1.05 |
| 疏水性值: | 0.87 |
| 外观与性状: | 白色粉末状固体 |
| 消光系数: | 5500 |
| 来源: | 人工化学合成,仅限科学研究使用,不得用于人体。 |
| 纯度: | 95%、98% |
| 盐体系: | 可选TFA、HAc、HCl或其它 |
| 生成周期: | 2-3周 |
| 储存条件: | 负80℃至负20℃ |
| 标签: | 未分类肽 |
背景
内皮素-1(ET-1)是内皮素家族主要的多肽,在血管和非血管组织参与多种生物学过程,包括心脏、肾脏和中枢神经系统。
在细胞水平,ET-1的作用是由ETA和ETB两个特定受体亚型介导的,这两者与磷脂酶C(PLC)功能上相耦合。
ET家族多肽的C-末端片段是高度保守序列,因为C末端片段仅激活ETB,可以用它来区分ETA和ETB的两个ET受体亚型。
参考文献:
1. Rubanyi, G. M., and M. A. Polokoff. Endothelins: molecular biology, biochemistry, pharmacology, physiology, and pathophysiology. Pharmacol. Rev. 46: 325–415, 1994
2. Simonson MS. Endothelins: multifunctional renal peptides. Physiol Rev 1993; 73: 375–411.
3. PM Vanhoutte Endothelin-1. A matter of life and breath, Nature, 368 (1994), pp. 693–694
多肽Ac-His-Leu-Asp-Ile-Ile-Trp-COOH的合成步骤:
1、合成CTC树脂:称取1.0g CTC Resin(如初始取代度约为0.31mmol/g)和0.37mmol Fmoc-Trp(Boc)-OH于反应器中,加入适量DCM溶解氨基酸(需要注意,此时CTC树脂体积会增大好几倍,避免DCM溶液过少),再加入0.93mmol DIPEA(Mw:129.1,d:0.740g/ml),反应2-3小时后,可不抽滤溶液,直接加入1ml的HPLC级甲醇,封端半小时。依次用DMF洗涤2次,甲醇洗涤1次,DCM洗涤一次,甲醇洗涤一次,DCM洗涤一次,DMF洗涤2次(这里使用甲醇和DCM交替洗涤,是为了更好地去除其他溶质,有利于后续反应)。得到 Fmoc-Trp(Boc)-CTC Resin。结构图如下:
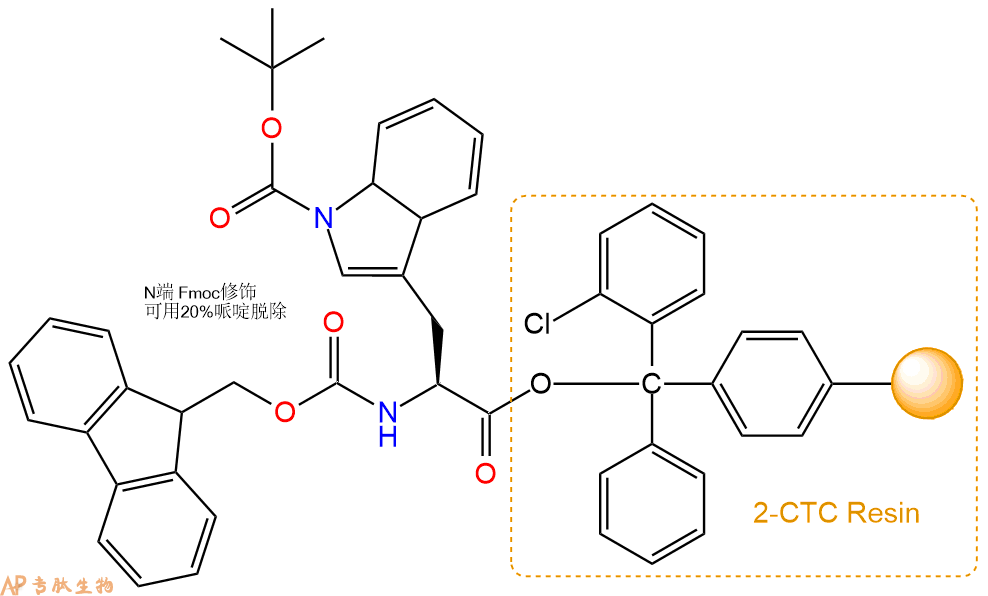
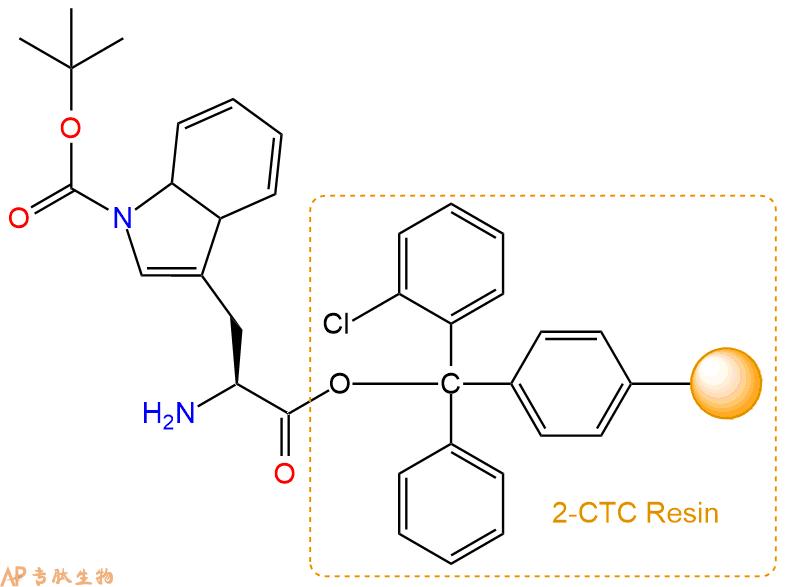
2、脱Fmoc:加3倍树脂体积的20%Pip/DMF溶液,鼓氮气30分钟,然后2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤5次。得到 H2N-Trp(Boc)-CTC Resin 。(此步骤脱除Fmoc基团,茚三酮检测为蓝色,Pip为哌啶)。结构图如下:
3、缩合:取0.93mmol Fmoc-Ile-OH 氨基酸,加入到上述树脂里,加适当DMF溶解氨基酸,再依次加入1.86mmol DIPEA,0.88mmol HBTU。反应30分钟后,取小样洗涤,茚三酮检测为无色。用2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤3次树脂。(洗涤树脂,去掉残留溶剂,为下一步反应做准备)。得到Fmoc-Ile-Trp(Boc)-CTC Resin。氨基酸:DIPEA:HBTU:树脂=3:6:2.85:1(摩尔比)。结构图如下:
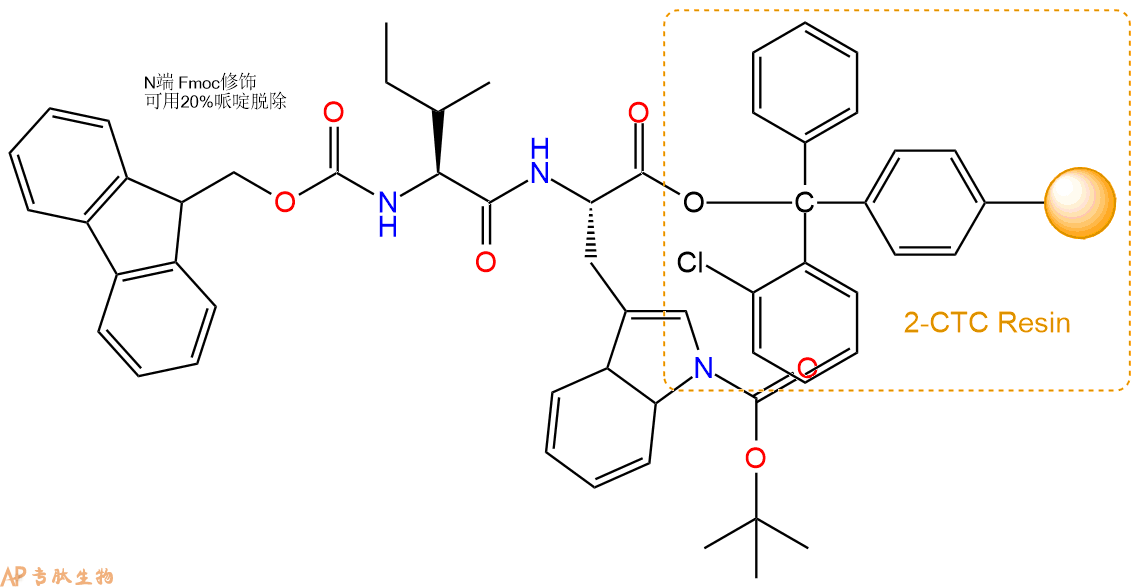
4、依次循环步骤二、步骤三,依次得到
H2N-Ile-Trp(Boc)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Ile-Ile-Trp(Boc)-CTC Resin
H2N-Ile-Ile-Trp(Boc)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Asp(OtBu)-Ile-Ile-Trp(Boc)-CTC Resin
H2N-Asp(OtBu)-Ile-Ile-Trp(Boc)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Leu-Asp(OtBu)-Ile-Ile-Trp(Boc)-CTC Resin
H2N-Leu-Asp(OtBu)-Ile-Ile-Trp(Boc)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-His(Trt)-Leu-Asp(OtBu)-Ile-Ile-Trp(Boc)-CTC Resin
以上中间结构,均可在专肽生物多肽计算器-多肽结构计算器中,一键画出。
最后再经过步骤二得到 H2N-His(Trt)-Leu-Asp(OtBu)-Ile-Ile-Trp(Boc)-CTC Resin,结构如下:
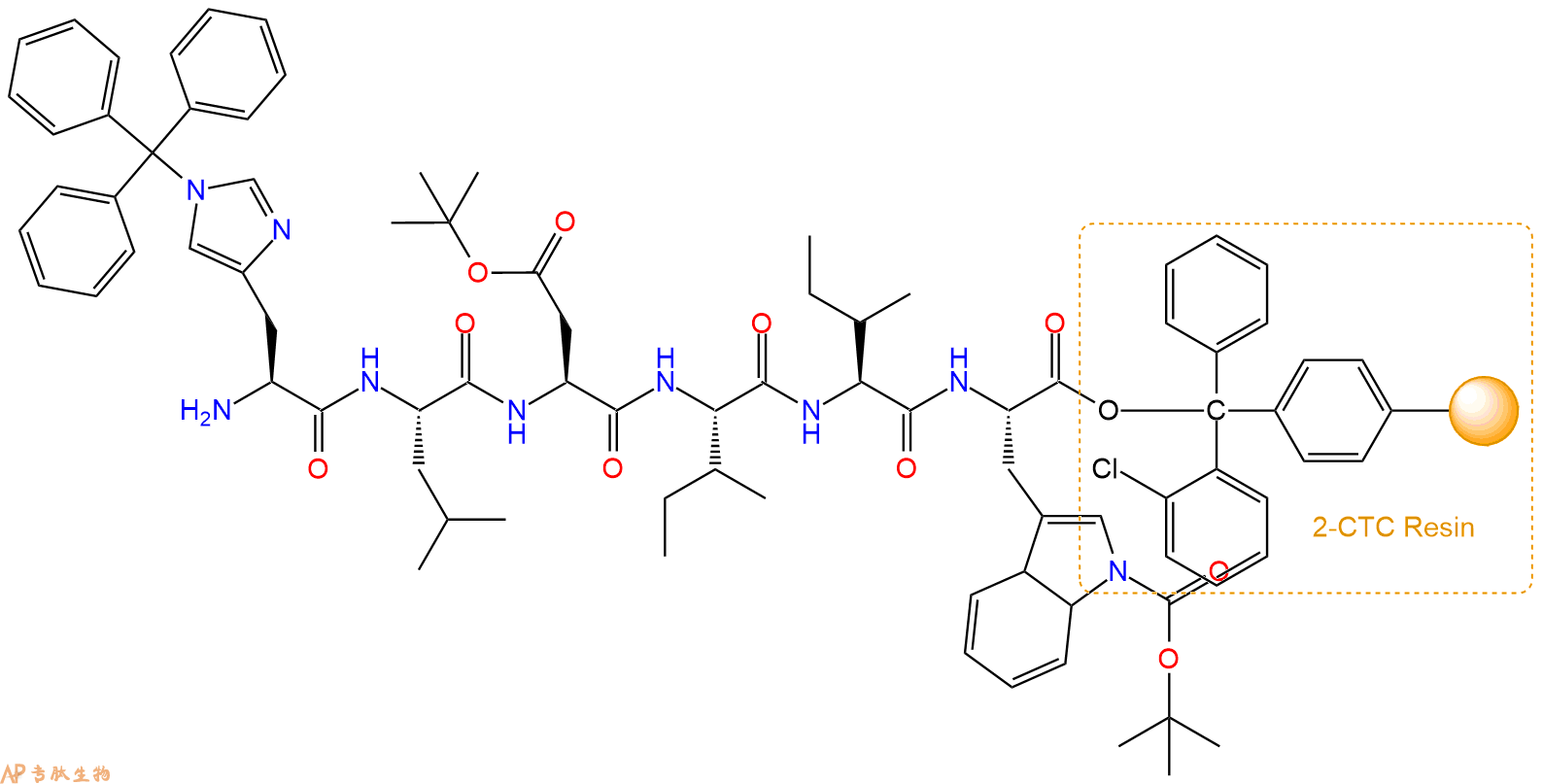
5、乙酸酐反应连接:在上述树脂中,加入适当DMF后,再加入0.93mmol乙酸酐到树脂中,再加入1.86mmol DIPEA,鼓氮气反应30分钟。用2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤3次树脂(洗涤树脂,去掉残留溶剂,为下一步反应做准备)。 得到Ac-His(Trt)-Leu-Asp(OtBu)-Ile-Ile-Trp(Boc)-CTCResin。 结构如下:
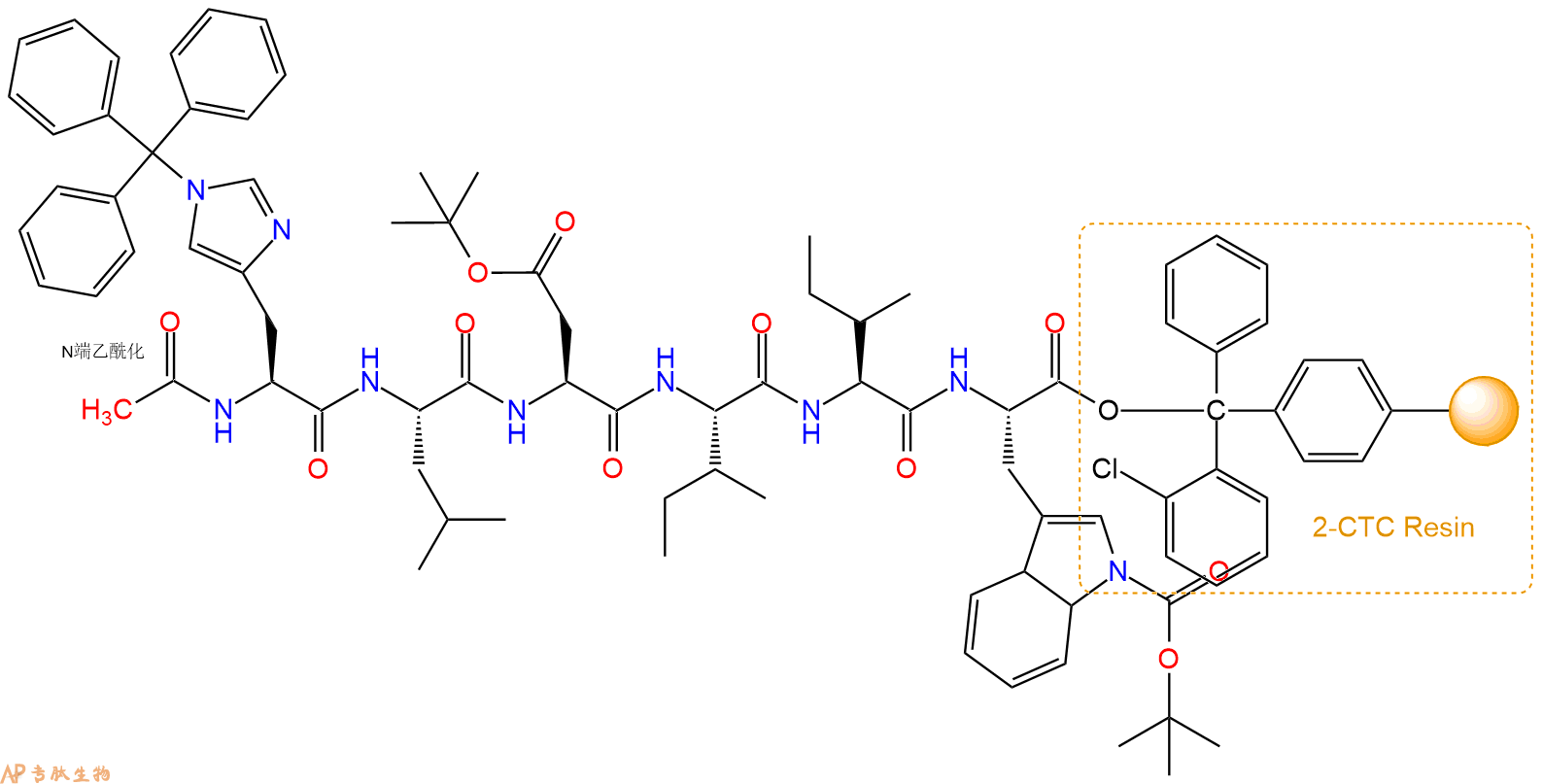
6、切割:6倍树脂体积的切割液(或每1g树脂加8ml左右的切割液),摇床摇晃 2小时,过滤掉树脂,用冰无水乙醚沉淀滤液,并用冰无水乙醚洗涤沉淀物3次,最后将沉淀物放真空干燥釜中,常温干燥24小试,得到粗品Ac-His-Leu-Asp-Ile-Ile-Trp-COOH。结构图见产品结构图。
切割液选择:1)TFA:H2O=95%:5%、TFA:H2O=97.5%:2.5%
2)TFA:H2O:TIS=95%:2.5%:2.5%
3)三氟乙酸:茴香硫醚:1,2-乙二硫醇:苯酚:水=87.5%:5%:2.5%:2.5%:2.5%
(前两种适合没有容易氧化的氨基酸,例如Trp、Cys、Met。第三种适合几乎所有的序列。)
6、纯化冻干:使用液相色谱纯化,收集目标峰液体,进行冻干,获得蓬松的粉末状固体多肽。不过这时要取小样复测下纯度 是否目标纯度。
7、最后总结:
杭州专肽生物技术有限公司(ALLPEPTIDE https://www.allpeptide.com)主营定制多肽合成业务,提供各类长肽,短肽,环肽,提供各类修饰肽,如:荧光标记修饰(CY3、CY5、CY5.5、CY7、FAM、FITC、Rhodamine B、TAMRA等),功能基团修饰肽(叠氮、炔基、DBCO、DOTA、NOTA等),同位素标记肽(N15、C13),订书肽(Stapled Peptide),脂肪酸修饰肽(Pal、Myr、Ste),磷酸化修饰肽(P-Ser、P-Thr、P-Tyr),环肽(酰胺键环肽、一对或者多对二硫键环),生物素标记肽,PEG修饰肽,甲基化修饰肽
以上所有内容,为专肽生物原创内容,请勿发布到其他网站上。